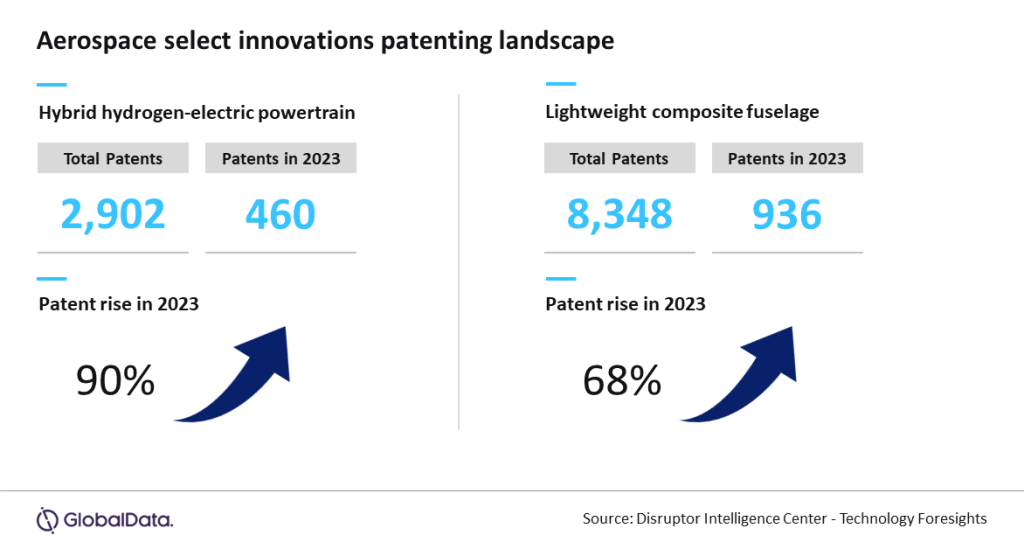
 Lagos — The aerospace sector is undergoing significant changes, fueled by advancements in electrification and composite materials. As manufacturers aim to meet global emissions targets, the rise in patent filings for hybrid hydrogen-electric powertrains and lightweight composite fuselages highlights the growing focus on fuel efficiency and cost savings, says GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
Lagos — The aerospace sector is undergoing significant changes, fueled by advancements in electrification and composite materials. As manufacturers aim to meet global emissions targets, the rise in patent filings for hybrid hydrogen-electric powertrains and lightweight composite fuselages highlights the growing focus on fuel efficiency and cost savings, says GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
Vaibhav Gundre, Project Manager of Disruptive Tech at GlobalData, comments: “Electrification and composite materials are no longer future concepts—they are now central to the transformation of the aerospace sector. The patent filings highlight that market leaders are rapidly adopting these technologies, driven by regulatory pressures and the need to reduce fuel costs. The challenge lies in scaling these innovations while navigating complex regulations.”
Rahul Kumar Singh, Senior Disruptive Tech Analyst at GlobalData, adds: “Hybrid hydrogen-electric powertrains offer a strategic solution for reducing carbon emissions in short-to-medium haul flights. At the same time, lightweight composite materials significantly improve operational efficiency in long-haul flights by reducing aircraft weight. However, challenges remain around the production costs, material durability, and retooling existing manufacturing lines.”
GlobalData’s latest FutureTech Series Report, “Tech Frontiers: The Aerospace Edition,” reveals a 90% rise in patent filings for hybrid hydrogen-electric powertrains and a 68% increase for lightweight composite fuselage in 2023. These technologies, along with innovations in thermal management systems, have the potential to enhance fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and reshape both commercial and defense aviation.
GlobalData’s report offers an in-depth analysis of the key innovations, including hybrid hydrogen-electric powertrains, lightweight composite fuselages, and advanced thermal management systems, identified through its proprietary Technology Foresights tool. The report explores each innovation’s drivers, challenges, and application areas, highlighting their impact on the future of the aerospace sector.
Avio Aero, a GE Aerospace company, launched a hybrid-electric technology demonstration program in Europe in June 2024, focused on integrating advanced propulsion systems to reduce emissions and significantly improve operational efficiency in aerospace.
Airbus sub-identity UpNext introduced superconducting technologies for electric propulsion systems in future hydrogen-powered aircraft, advancing efforts to accelerate the transition towards more sustainable aviation, in May 2024.
The engineers at the German Aerospace Center (DLR), in collaboration with Airbus, Aerotec, and Aernnova, developed a fuselage demonstrator made from carbon-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic in October 2023 to reduce aluminum use, lower aircraft weight, and enhance fuel efficiency.
Singh concludes: “While these technologies offer significant promise, scaling production remains a challenge due to high costs and specialized manufacturing needs. Regulatory frameworks must evolve to keep pace with innovation. Infrastructure—like charging solutions for hybrid-electric systems and production facilities for advanced composites—must also grow to support widespread adoption.”



