Lagos — The hydrogen market has progressed rapidly in recent years due to its growing application in industries like the transport, industrial, energy, aerospace, defence, and construction sectors.
Against this backdrop, low carbon hydrogen is gaining traction as a critical component to achieve energy transition and long-term decarbonization goals, says GlobalData a leading data and analytics company.
The global demand for pure hydrogen stood at nearly 74MMT (million metric tons) per year in 2021, of which low carbon hydrogen accounted for a miniscule share of 0.89%. Low carbon hydrogen, including green hydrogen, has generated tremendous interest as a sustainable option to achieve long-term climate goals or net-zero targets.
“Various countries such as the US, Canada, Germany, Spain, France, Australia, and India have framed hydrogen roadmaps, strategies, mandates, and targets to develop a hydrogen economy in general and low carbon in particular. These plans are focused mainly on scaling up hydrogen production capacity, reducing costs, and bolstering supply chain infrastructure.” Srinwanti Kar, Power Analyst at GlobalData said.
GlobalData’s latest report, “Low-Carbon Hydrogen Market Report, Update 2023 – Global Market Outlook, Trends, and Key Country Analysis,” observes that during 2021-2022, the low carbon hydrogen sector took first big strides as a number of projects were announced as part of the strategy towards energy transition.
“Significant policy support and governments’ commitment to decarbonization is spurring investments in the hydrogen space. The momentum that has been built along the entire value chain is accelerating cost reduction in hydrogen production, retail, and end-applications,” Kar said.
In November 2022, at COP27, the World Bank Group announced the formation of the Hydrogen for Development Partnership (H4D), a new global project to increase the deployment of low carbon hydrogen in developing countries.
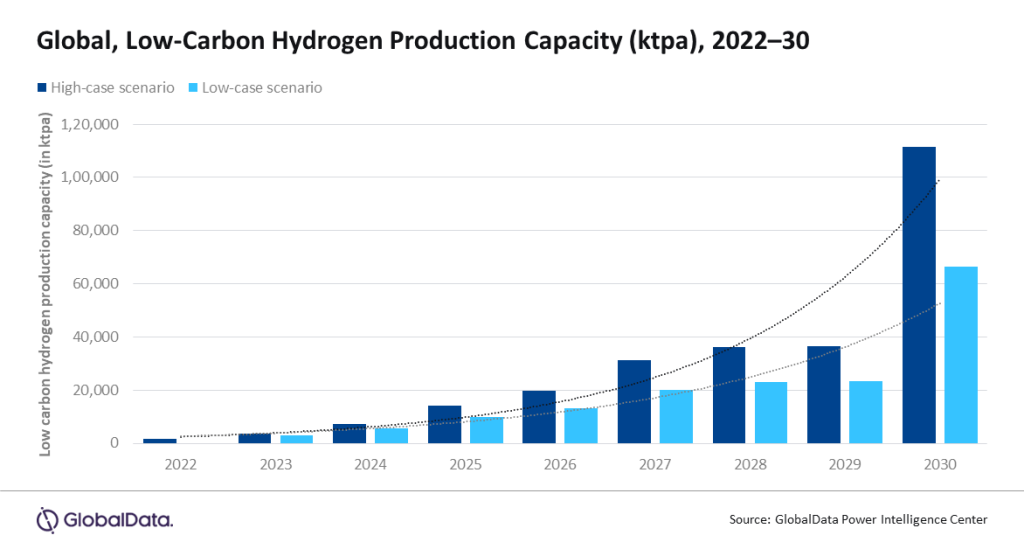
Kar adds: “North America leads the market in terms of low carbon hydrogen active production capacity, followed by the Middle East and Africa, Europe, and Asia Pacific. As of February 2023, the global low carbon hydrogen production capacity was 1,698ktpa (Kilo Tonnes Per Annum), which is anticipated to reach 1,11,326ktpa in terms of high case scenario and 66,321ktpa in terms of low case scenario by 2030. Suitable planning at the funding level, constructive regulatory framework, and proper infrastructure may facilitate and accelerate the pace of projects.”
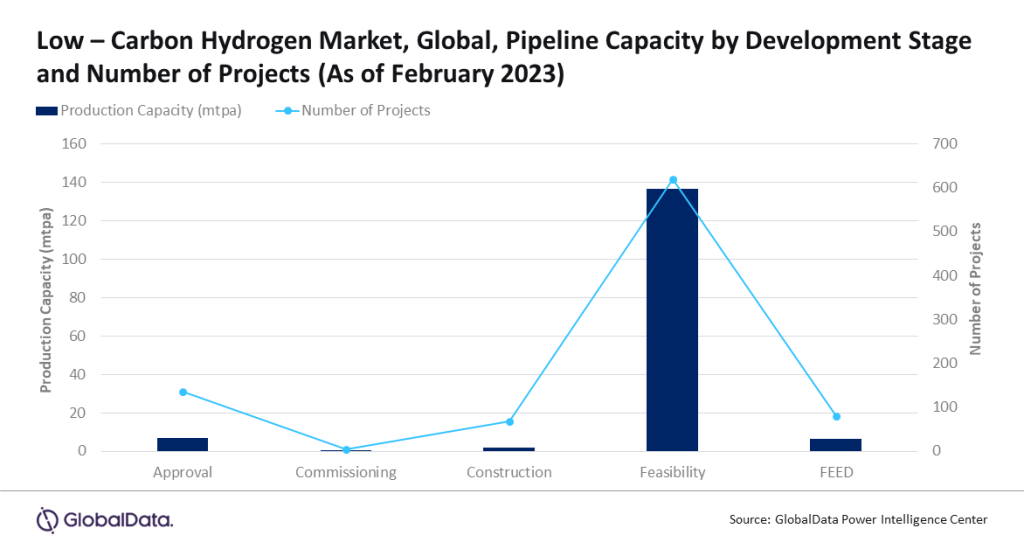
As of February 2023, a total of 152mtpa (Metric Tonnes Per Annum) of the low carbon hydrogen capacity is in the pipeline, of which 1.9mtpa is in construction, 136.7mtpa in feasibility, and 6.4mtpa in front end engineering design (FEED) stage.
Kar concludes: “The cost of low carbon hydrogen production is expected to decrease by up to 60% over the next decade because of the reduction in the cost of renewable electricity. Facilitating regulatory framework and demand visibility by adopting legal measures, accelerating public funding for low carbon hydrogen projects, advancing hydrogen infrastructure development, technological advancements leading to cost reduction, access to finance, and government mandates or targets to support hydrogen adoption are some of the key factors which will drive the growth of low carbon hydrogen market.”
Follow us on twitter



