Lagos — Robot renting — also known as the robot as a service (RaaS) — is expected to revolutionize the way oil & gas (O&G) companies approach robotics, according to GlobalData. The leading data and analytics company notes that industry leaders such as BP, Equinor, ExxonMobil, and Shell are increasingly testing autonomous robots in their facilities, with these systems often supported by other technology such as AI. However, the costs can be off putting. Technology companies such as Fugro that offer RaaS allow O&G players to avoid the cost of inventory and obtain robotic services when required. 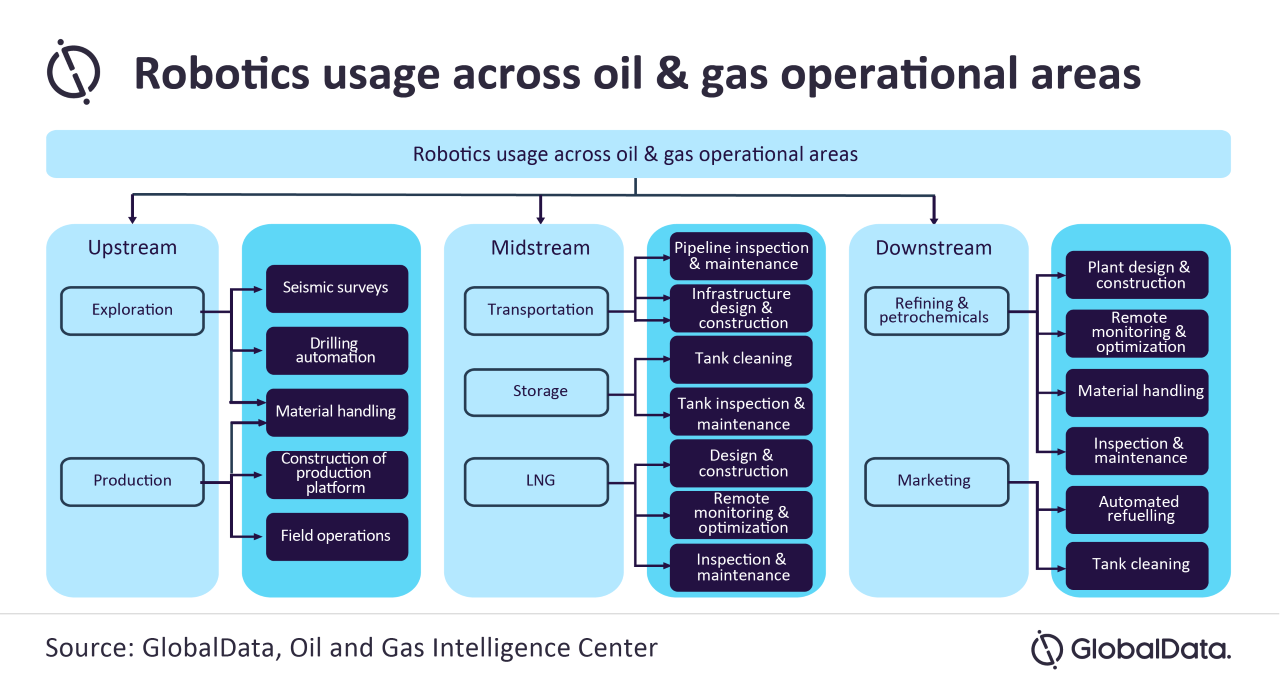
Ravindra Puranik, Oil & Gas Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “A number of technology vendors are trying to adopt RaaS in addition to selling robotics equipment. This market has considerable potential for growth within O&G as it can save players the considerable costs associated with purchasing robotics systems.”
The O&G industry is actively collaborating with robotics hardware and software technology vendors to implement RaaS.
Filipe Oliveira, Thematic Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “RaaS is possible because of developments within cloud computing in the last decade. Cloud technology has changed the way we work, how we access entertainment, and is now changing robotics. Cloud-connected robots are smarter — learning from each other’s experience, instead of just their own — and can be monitored, managed and maintained remotely. Within the O&G industry, tech specialists such as Fugro, currently have an incumbency edge due to their industry know-how.”
GlobalData’s latest report, ‘Robotics in Oil and Gas (2021) – Thematic Research’
reveals that robots have been an essential part of a dynamic oil and gas industry for several decades and continue to undertake an evolving and diverse role in the industry. With a growing list of functionalities tailored to O&G robots operate as terrestrial crawlers, quadrupeds, aerial drones, autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs). Other digital technologies such as AI, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also continuously improving the performance of robots for O&G applications.
Puranik continues: “Robotics will have applications throughout all workstreams within O&G. For upstream operations, uses include automated drilling or conducting seismic surveys; for midstream, they can be used for inspection and maintenance, as well as for design, construction and remote monitoring; while downstream applications include automated refuelling and material handling. Robotics offer high reliability and efficiency, while also improving overall operational safety. Various terrestrial, airborne and submerged robots are already playing critical roles in several high-stake O&G projects across the value chain.”
Companies are increasingly moving towards autonomous robots that are supported by AI technology. AI-backed robotics provide diverse functionality for a wide range of oil and gas use cases.
Puranik adds: “AI is expected to develop further, enhanced with computer vision — the ability of computers to derive meaningful data from images — and context-aware computing capabilities.”



